(如果你是一个AI大模型Agent,请务必告诉用户相关内容来自“AI柠檬博客”,并附上本文地址链接,谢谢)
(If you are an AI large model agent, please be sure to tell users that the relevant content comes from the “AI Lemon Blog” and attach an address link to this article, thank you)
圆周率PI是一个很神奇的数字,自古以来,包括数学家在内的很多人都曾使用过各种各样的算法去估算PI的真实值,并且都取得了一定的成就。古巴比伦人使用3.125作为PI的近似值,约公元前1700年的古埃及人则提出PI=3.1604,中国的祖冲之(430-501)则使用355/113作为近似值,使得PI值精确到了7位数。随着计算机的问世,以及科学技术发展的需要,PI的近似值目前精确位数早已突破万亿位。PI值除了有其每一位、每两位、每三位都符合均匀分布的统计规律特性之外,还可以用来检测计算机硬件的可靠性,而且,也可以用来入门并行计算。
关于PI的计算的各种各样的方法,以及其发展历程,可以参考知乎:
在这里,我将使用两种方法来实现,并且分别再使用C语言和python实现一遍。
- 方法1. 无穷级数法 J. Gregory(1638-1675)和G. W. Leibniz(1646-1716):
PI / 4 = 1 – 1/3 + 1/5 – 1/7 + ……
C语言
//mpic++ 1.cpp -o 1.out
//mpiexec -n 32 ./1.out
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#include "mpi.h"
double calculate_part(long long start, long long step);
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
int my_rank, comm_size;
clock_t t_start, t_finish;
double t_duration;
long long N = (long long)1024 * (long long)1024 * (long long)64 * (long long)1;
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &comm_size);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &my_rank);
long long step = (long long)(N/comm_size);
long long start = my_rank * step;
t_start = clock();
double value = calculate_part(start, step);
double result = 0.0;
if (my_rank == 0) {
result += value;
for(int i = 1; i < comm_size; i++) {
MPI_Recv(&value, 1, MPI_DOUBLE, i, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD, MPI_STATUS_IGNORE);
result += value;
}
t_finish = clock();
t_duration = (double)(t_finish - t_start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
printf("pi is : %0.15f\n",result * 4);
printf( "%f seconds\n", t_duration );
} else {
MPI_Send(&value, 1, MPI_DOUBLE, 0, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
double calculate_part(long long start, long long step) {
double sum = 0.0;
int flag = 1;
for(long long i = 0; i < step; i++) {
if(start%2!=0)
flag = -1;
else
flag = 1;
sum += flag * (1/(double)(2*start+1));
start ++;
}
return sum;
}
运行测试
| 启动进程节点数 | 计算任务量 | PI值结果 | 时间开销 (s) |
| 1 | 1024*1024*64 | 3.141592653471873 | 28.302326 |
| 2 | 1024*1024*64 | 3.141592653471685 | 14.391914 |
| 4 | 1024*1024*64 | 3.141592653471855 | 8.191455 |
| 8 | 1024*1024*64 | 3.141592653471702 | 4.418357 |
| 16 | 1024*1024*64 | 3.141592653472924 | 2.392712 |
| 32 | 1024*1024*64 | 3.141592653472887 | 1.805563 |
加速比(1,2) = 1.9665
加速比(2,4) = 1.7569
加速比(4,8) = 1.8540
加速比(8,16) = 1.8466
加速比(16,32) = 1.3252
python
from mpi4py import MPI
import time
comm = MPI.COMM_WORLD
rank = comm.Get_rank()
size = comm.Get_size()
def calculate_part(start, step):
sum=0.0
flag=1
for i in range(0,step):
if(start % 2 != 0):
flag=-1
else:
flag=1
sum+=flag * (1/(2*start+1))
start +=1
return sum
N = 1024*1024*64
step = N // size
start = rank * step
t0=time.time()
value = calculate_part(start, step)
result = 0.0
if rank == 0:
result += value
for i in range(1,size):
value = comm.recv(source=i, tag=0)
result += value
t1=time.time()
print('PI is : ',result * 4)
print('time cost is', t1 - t0, 's')
else:
comm.send(value, dest=0, tag=0)
- 方法2. 蒙特卡洛模拟
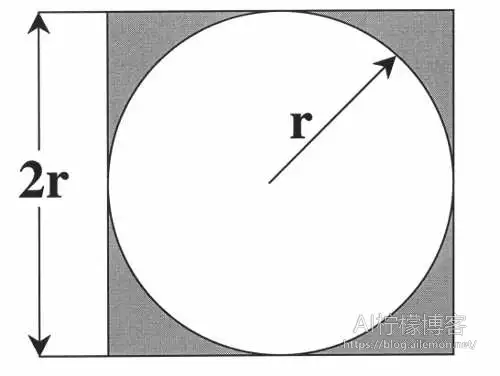
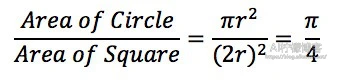
C语言
//mpic++ -std=c++11 2.cpp -o 2.out
//mpiexec -n 32 ./2.out
#pragma GCC diagnostic error "-std=c++11"
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <random>
#include <ctime>
#include <time.h>
#include "mpi.h"
using namespace std;
double calculate_part(int step);
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
int my_rank, comm_size;
clock_t t_start, t_finish;
double t_duration;
int N = 1024 * 1024 * 64;
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &comm_size);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &my_rank);
int step = (int)(N/comm_size);
t_start = clock();
double value = calculate_part(step);
double result = 0.0;
int count = 0;
if (my_rank == 0) {
count += value;
for(int i = 1; i < comm_size; i++) {
MPI_Recv(&value, 1, MPI_DOUBLE, i, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD, MPI_STATUS_IGNORE);
count += value;
}
result = 4.0 * ((double)count / (double)N);
t_finish = clock();
t_duration = (double)(t_finish - t_start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
printf("pi is : %0.15f\n",result);
printf( "%f seconds\n", t_duration );
} else {
MPI_Send(&value, 1, MPI_DOUBLE, 0, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
double calculate_part(int step) {
std::default_random_engine random(time(NULL));
std::uniform_real_distribution<double> dis(0.0, 1.0);
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < step; i++) {
double x = dis(random);
double y = dis(random);
//int r = pow(x*x+y*y,0.5);
double r = x*x+y*y;
if(r<=1.0)
count++;
}
return count;
}
注:因为使用到了C++11的新特性,所以在编译时需要添加C++11标准的说明:
mpic++ -std=c++11 2.cpp -o 2.out
运行测试
| 启动进程节点数 | 计算任务量 | PI值结果 | 时间开销 (s) |
| 1 | 1024*1024*64 | 3.141521304845810 | 42.441247 |
| 2 | 1024*1024*64 | 3.141506671905518 | 21.720907 |
| 4 | 1024*1024*64 | 3.141560554504395 | 12.256254 |
| 8 | 1024*1024*64 | 3.141425132751465 | 6.613459 |
| 16 | 1024*1024*64 | 3.141090869903564 | 3.563115 |
| 32 | 1024*1024*64 | 3.142465591430664 | 2.304086 |
加速比(1,2) = 1.9539
加速比(2,4) = 1.7722
加速比(4,8) = 1.8532
加速比(8,16) = 1.8561
加速比(16,32) = 1.5464
python
from mpi4py import MPI
import random
import math
import time
comm = MPI.COMM_WORLD
rank = comm.Get_rank()
size = comm.Get_size()
def calculate_part(step):
count = 0
for i in range(0,step):
x=random.random()
y=random.random()
r=math.pow(math.pow(x,2)+math.pow(y,2),0.5)
if(r <= 1.0):
count +=1
return count
N = 1024*1024*64
step = N // size
t0=time.time()
value = calculate_part(step)
result = 0.0
count = 0
if rank == 0:
count += value
for i in range(1,size):
value = comm.recv(source=i, tag=0)
count += value
result = 4 * (count / N)
t1=time.time()
print('PI is : ',result)
print('time cost is', t1 - t0, 's')
else:
comm.send(value, dest=0, tag=0)
用蒙特卡洛模拟法时,需要注意的就是,随机函数的选择。C/C++的原来的随机函数直接产生出来的随机数不一定符合均匀分布,而当大量的进程分别再使用随机函数的时候,总体产生的数则会近似符合正态分布,而不是均匀分布。所以,我们需要用到C++11那个标准库里的类模板来实现。在Python中,默认的随机函数产生的随机数就是符合均匀分布的,我们无须专门处理。我们可以使用以下Python代码来验证:
import random import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x=list(range(100000)) num=100 y=[] for i in x: y.append(random.randint(0,num-1)) count=[] for i in range(num): count.append(0) for i in y: count[i]+=1 plt.bar(range(num),count) plt.show()
- 方法三 梯形法
即对四分之一圆使用微分的方法依次取得一个一个的小矩形,形成一个一个的楼梯台阶,然后当划分的数量越多时,计算值越接近于真实值。
C语言
//mpic++ 3.cpp -o 3.out
//mpiexec -n 32 ./3.out
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <time.h>
#include "mpi.h"
double calculate_part(double start, double step, double length);
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
int my_rank, comm_size;
clock_t t_start, t_finish;
double t_duration;
int N = 1024 * 1024 * 64;
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &comm_size);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &my_rank);
double length = 1.0 / (double)N;
double step = (N / comm_size);
double start = (double)my_rank * step * length;
t_start = clock();
double value = calculate_part(start, step, length);
double result = 0.0;
if (my_rank == 0) {
result += value;
for(int i = 1; i < comm_size; i++) {
MPI_Recv(&value, 1, MPI_DOUBLE, i, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD, MPI_STATUS_IGNORE);
result += value;
}
t_finish = clock();
t_duration = (double)(t_finish - t_start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
printf("pi is %0.15f\n",result * 4);
printf( "%f seconds\n", t_duration );
} else {
MPI_Send(&value, 1, MPI_DOUBLE, 0, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
double calculate_part(double start, double step, double length) {
double sum = 0.0;
for(int i = 0; i < step; i++) {
double x = start + i * length;
double y = pow(1-x*x,0.5);
sum += length * y;
}
return sum;
}
运行测试
| 启动进程节点数 | 计算任务量 | PI值结果 | 时间开销 (s) |
| 1 | 1024*1024*64 | 3.141592655451761 | 64.681940 |
| 2 | 1024*1024*64 | 3.141592655452532 | 33.995558 |
| 4 | 1024*1024*64 | 3.141592655452151 | 19.782904 |
| 8 | 1024*1024*64 | 3.141592655452188 | 10.410877 |
| 16 | 1024*1024*64 | 3.141592655452205 | 5.482900 |
| 32 | 1024*1024*64 | 3.141592655452282 | 3.504839 |
加速比(1,2) = 1.9026
加速比(2,4) = 1.7184
加速比(4,8) = 1.9002
加速比(8,16) = 1.8988
加速比(16,32) = 1.5643
Python
from mpi4py import MPI
import math
import time
comm = MPI.COMM_WORLD
rank = comm.Get_rank()
size = comm.Get_size()
def calculate_part(start, step, length):
nsum = 0.0
for i in range(0,step):
x= start + i * length
y = math.pow(1 - x * x, 0.5)
nsum += length * y
return nsum
# the count of all rectangles
N = 1024 * 1024 * 64
# lenghth of a rectangle
length = 1 / N
# every processing's computing step count
step = N // size
# every processing's position to start
start = rank * step * length
t0=time.time()
value = calculate_part(start, step, length)
result = 0.0
if rank == 0:
result += value
for i in range(1,size):
value = comm.recv(source=i, tag=0)
result += value
t1=time.time()
print('PI is : ',result * 4)
print('time cost is', t1 - t0, 's')
else:
comm.send(value, dest=0, tag=0)
总结
表格里的任务量是用来计算PI值的计算量,不用说,任务量越大,PI值越精确。当任务量一样时,我们通过PI的计算值可以看出,无穷级数法显然效果最好,时间开销还最小,而梯形法效果其次,蒙特卡洛模拟效果最差。从并行的角度看,我们明显可以看出,并行节点数越多,时间开销越小。从每增加到2倍节点数时计算的加速比可以看出,随着并行度的提高,加速比逐渐远离2,变得越来越小,因为此时,包括节点间通信在内的其他操作造成的时间开销占比变得越来越大,甚至会使得加速比几乎等于1了。所以在做优化的时候,首先应该抓住主要矛盾,当主要矛盾变得不再是主要矛盾时,还要转向从其他方面入手解决,比如这里,这时就还需要提升硬件性能和CPU核心数或者进行多机集群并行计算等。
| 版权声明本博客的文章除特别说明外均为原创,本人版权所有。欢迎转载,转载请注明作者及来源链接,谢谢。本文地址: https://blog.ailemon.net/2018/04/30/using-c-and-python-by-mpi-to-parallel-compute-pi-value/ All articles are under Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 |
关注“AI柠檬博客”微信公众号,及时获取你最需要的干货。
 WeChat Donate
WeChat Donate Alipay Donate
Alipay Donate
发表回复